Bitcoin Mining Goes Institutional – But Can It Survive Tariffs, AI Grid Wars, and Fee Collapse?
In 2025, Bitcoin mining is no longer just a competition over hashpower and block rewards—it has evolved into a full-scale infrastructure war, where access to energy, geopolitical positioning, and integration with emerging technologies like AI define who survives and who fades out.
According to the newly released Bitcoin Mining Market Review and Key Trends authored by Nico Smid, research analyst at GoMining Institutional, and Fakhul Miah, managing director at GoMining Institutional, the industry now finds itself locked in a struggle with one of the world’s fastest-growing tech verticals: artificial intelligence.
AI hyperscalers are demanding huge amounts of electricity for model training and deployment, putting them on a direct collision course with Bitcoin miners, who also rely on affordable, high-volume power to remain profitable.
This competition has triggered what the report calls a “power crunch,” forcing mining companies to rethink site selection, energy procurement, and geopolitical risk in real time.
The competition for electricity is no longer limited to internal mining rivalries—it has gone external. Major players like Riot Platforms have paused a 600 MW expansion, while Iris Energy has shifted away from pure BTC mining to allocate capacity toward AI cloud services.
On February 13, Riot Platforms also announced that it is actively pursuing potential partnerships within the AI and HPC sectors.
As nations attempt to balance power grids and prioritize forward-looking technologies, miners are being priced out, regulated against, or simply pushed aside, claims the report.
Institutional Capital Pours in, but Miners Are Squeezed
The report notes that this crunch comes at a time when institutional demand for Bitcoin has never been higher. Wall Street has poured billions into U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs, and the U.S. government has officially recognized the asset by forming a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve.
The result is a paradox: demand for Bitcoin is soaring, but the supply-side infrastructure—mining—is becoming more fragile.
While capital floods into ETFs, miners face rising operating costs, compressed fees, and restricted energy access. Hash price has declined sharply post-halving, and transaction fee revenue has collapsed to less than 1% of miner income.
Even as Bitcoin becomes more embedded in institutional portfolios and public balance sheets, the ability to mint new coins is under siege. This growing disconnect between Bitcoin’s financialization and the economic sustainability of mining is one of the report’s core warnings.
Miners Turn to Financial Engineering to Survive
To survive this high-cost, post-halving environment, miners are evolving into financial tacticians. No longer just hardware operators, leading firms are now using Bitcoin-backed loans, convertible notes, and creative equity structures to raise capital without liquidating their BTC reserves.
The report identifies this trend as “the rise of the financially engineered miner,” where the ability to model capital stack scenarios is as important as mining efficiency.
The shift marks a turning point in how mining companies operate. Access to energy is still paramount, but access to capital markets—and the sophistication to operate within them—is now equally essential.
As mining companies adapt to lower margins and greater volatility, their financial survival may hinge on how well they can balance debt, equity, and retained BTC while preparing for further pressure from AI, regulation, and tariffs.
Legacy Hardware Feels the Pain
The report also shines a light on the economic pressure facing legacy ASIC hardware. The S19 generation of miners, which still accounts for roughly 25% of Bitcoin’s total hashrate, is fast approaching obsolescence.
Profitability data shows that S19 units operating at electricity costs above $0.06/kWh are already unprofitable unless the hash price exceeds $60—a rarity in 2025. For operators paying more than $0.05/kWh, even slight hash price drops can push them into the red.
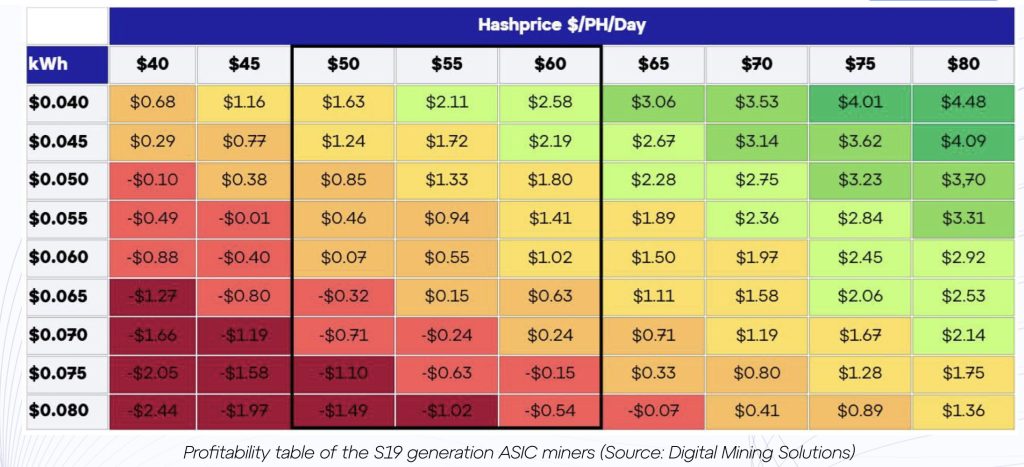
While the S19 has been a workhorse since its release five years ago, it is now a liability for many mining farms. The narrowing profit margins are an indicator of how quickly economic viability can shift, particularly in an industry facing both internal halving events and external competition from AI infrastructure players, GoMining Institutional reports.
Outlook: More Than Just Block Rewards
The report concludes that the first half of 2025 has revealed that Bitcoin mining is no longer a closed system. It’s now a frontline industry operating at the intersection of capital, energy, and compute.
As the network seeks equilibrium after April’s halving, miners must make tough decisions about scale, strategy, and survival.
The second half of the year promises no less intensity—but the winners will be those who can work within capital markets as well as they can manage hashpower.
You May Also Like

Cashing In On University Patents Means Giving Up On Our Innovation Future

VectorUSA Achieves Fortinet’s Engage Preferred Services Partner Designation

