Everything You Need to Know About Dead Code
What Is "Dead Code"?
Dead code refers to parts of a codebase that are written but never executed, called, imported, or otherwise needed during the normal operation of the application.
Over time, as features are added, changed, or removed, some code becomes obsolete but is accidentally left behind. This can lead to:
- Increased bundle size
- Slower build times
- Harder maintenance and onboarding
- Potential security risks
Cleaning up unused code improves clarity, performance, and long-term maintainability.
What Is Considered "Dead Code"?
Here are the common categories of unused code:
-
Unused Variables
Declared but never used in any operation.
-
Unused Functions or Methods
Defined but never called anywhere.
-
Unused Imports
Imported modules or packages that are never referenced.
-
Unused Exports
Functions or components exported from a module but not imported elsewhere.
-
Unused Files
Complete files (components, modules, etc.) that are never imported or required.
-
Unused Dependencies
Libraries listed in your package manager (e.g.,
package.json) that are not imported or used in the codebase.
Some exceptions:
-
Disabled Features
Features that are temporarily disabled or taken out, but will be used in the future.
-
Helper functions
Utility functions that help with common tasks can be reviewed regularly to check if it needs to be removed.
Tools for Scanning Dead Code
The following tools help detect and analyze unused code, imports, functions, variables, and dependencies. Choose tools based on your tech stack:
- ts-prune
- Detects unused exported functions, constants, and types in TypeScript projects.
- On Maintenance (no further update)
- depcheck
- Checks for unused npm dependencies and missing ones.
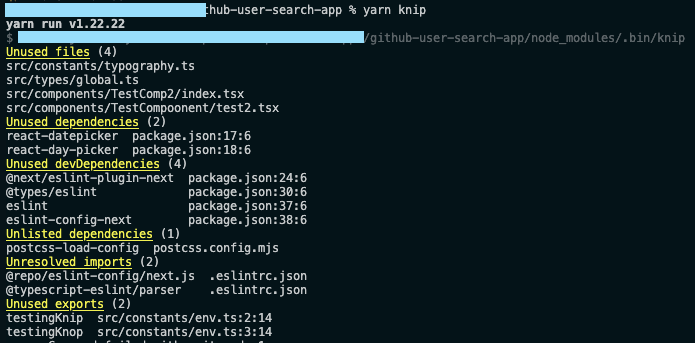
- knip.dev (We are using this!)
- Knip finds and fixes unused dependencies, exports and files in your JavaScript and TypeScript projects. Less code and dependencies lead to improved performance, less maintenance and easier refactorings.
How to Scan and Remove Unused Code with knip
Follow these steps to identify and safely remove unused code from your project using knip:
- Install
knip(if not already installed):
yarn add -D knip # or npm install -D knip - Run the analysis:
yarn knip Note: Replace yarn with your preferred package manager (npm, pnpm, etc.).
\
-
Review the list of unused files or exports:
-
Go through the list from top-down, starting with high-level components, constants, and utilities.
-
Search your codebase to verify whether each flagged file or export is truly unused.
- If it's used elsewhere, skip it.
- If it has no references, it’s safe to delete.
-
Remove confirmed dead code
-
Delete unused files, exports, or lines confidently after reviewing
-
Check with your teammates if the components/files is not used anymore or just temporarily not used
-
Validate your codebase:
-
Run linters and TypeScript checks to catch any issues:
yarn lint npx tsc --noEmit -
Start the development server to confirm everything still works:
yarn dev -
Final step: Commit your changes with a clear message, e.g.:
git commit -m "chore: remove unused code and dependencies" Getting rid of dead code might feel like a chore, but it’s totally worth it. Cleaner code means fewer headaches, faster builds, and easier debugging down the line. With the right tools and a step-by-step approach, it’s not that hard to keep your codebase in shape. If you’re working in a fast-paced company where keeping track of all the new code is challenging, making this part of your regular workflow is a must.
If you have any other better approach or just want to share your own process, feel free to share in the comment! I would love to hear your thought!
You May Also Like

Chinese Bitcoin Hardware Titans Control 95% of Market, Now Coming to America to Dodge Trump Tariff War

Analysis: The number of new Bitcoin wallet addresses has stabilized, and whale accounts and institutional funds dominate the market